What is the circuit breaker?
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-08 Origin: Site








A circuit breaker works like a safety switch in an electrical system. You can think of it as a traffic cop for electricity. If too much current tries to go through the wires, the circuit breaker stops it. This keeps people and property safe from harm.
Circuit breakers act fast when there are abnormal surges. These surges can be overloads or short circuits. These problems often cause electrical fires. The quick action of circuit breakers stops overheating. This lowers the risk of danger.
| Circuit Breaker Type | Instantaneous Tripping Current (Multiples of Rated Current) |
|---|---|
| B | 3 to 5 times rated current |
| C | 5 to 10 times rated current |
| D | 10 to 14 times rated current |
| K | 8 to 12 times rated current |
| Z | 2 to 3 times rated current |
A circuit breaker protects by turning off power by itself when it senses danger. People can reset it after the problem is fixed.
Key Takeaways
Circuit breakers work like safety switches. They stop too much electricity. This helps protect people and property from fires and shocks. They find problems like overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. Then they quickly turn off the power to stop damage. Picking the right type and size of circuit breaker is important. Checking it often keeps electrical systems safe and working well. Circuit breakers can be reset after they trip. This makes them easier and cheaper to use than fuses. New smart circuit breakers use real-time data. They have advanced features to make things safer and stop power outages.
Circuit Breaker Purpose
Electrical Safety
A circuit breaker is very important for electrical safety in buildings. Its main job is to keep people and property safe from electrical dangers. When too much electricity tries to move through a wire, the circuit breaker notices the problem and stops the current. This helps stop fires, shocks, and other bad accidents.
You can think of circuit breakers like traffic cops for electricity. They watch the current inside the electrical panel. If something goes wrong, like a short circuit or ground fault, the breaker acts fast. It stops the flow, just like a cop stopping cars from going down a blocked road. This quick action is called short circuit protection. It keeps everyone safe by stopping dangerous currents from reaching outlets or appliances.
Tip: Always pick the right circuit breaker for your system. The right choice and good installation give the best protection.
International rules, like those from the IEC, say circuit breakers must trip if current gets too high. These rules make sure every over-current protection device works right. Miniature circuit breakers use both heat and magnets to find problems. They trip when needed, stopping the flow and keeping people safe.
Preventing Damage
Circuit breakers also protect equipment, not just people. They help stop damage to electrical devices. Overload protection is one of their main jobs. If too many things use power at once, wires can get too hot. The circuit breaker’s job is to notice this and turn off the power before anything breaks.
Engineering studies show that planning and regular checks make circuit breakers work better. Load flow and short circuit tests help experts choose the right breaker size. These tests also find weak spots in the system. Fixing these problems early stops equipment from breaking and saves money.
A recent study showed that checking and replacing circuit breakers on time lowers the risk of overloads. Utilities that test their breakers often find problems before they cause blackouts or damage. For example, one big utility stopped a huge outage by changing a worn breaker after a test. Taking care of breakers like this saves money and keeps the lights on.
| Protective Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Stops current when too many things use power, so wires do not overheat. |
| Short Circuit Protection | Stops current right away during faults, so fires and equipment loss do not happen. |
| Ground Fault Protection | Finds leaks to ground and trips to stop shocks and other dangers. |
Circuit breakers need to fit the system’s needs. Picking the right one and testing it often keeps it ready to work. This careful way makes sure every circuit breaker can stop overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
How Circuit Breakers Work
Key Components
Every circuit breaker has important parts that work together. The frame keeps all the parts safe and in place. Contacts open or close to let electricity move or stop. The trip unit looks for problems like too much current or a short circuit. The operating mechanism moves the contacts when the trip unit finds a problem.
Modern circuit breakers have new features for better safety. Some have arc flash protection and ground fault detection. These features help stop dangerous problems before they cause harm. Data centers and other big buildings need these features to meet strict rules like NFPA 70E and NFPA 70B. New technology like IoT, AI, and EPMS lets people watch the system in real time. These tools help experts find problems early and keep the circuit breaker working well.
Note: Picking the right circuit breaker design makes sure all parts work together. This helps stop failures and keeps the system safe.
Reports from experts show that updating circuit breakers makes them safer and more reliable. These reports say it is important to upgrade key parts to avoid problems. Experts also say to check and update breakers often. This keeps them working well and stops surprise failures.
Tripping Mechanism
The tripping mechanism is the main part that protects electrical systems. When the trip unit finds a problem, it tells the operating mechanism to act. The contacts then open and stop the electricity. The circuit breaker goes into a time-out state. This pause lets the system rest and stops more damage.
Circuit breakers use two ways to find problems: thermal and magnetic. The thermal way uses a metal strip that bends when it gets hot. If it bends enough, it trips the breaker. The magnetic way uses a coil that makes a strong field during a surge. This field pulls a lever and trips the breaker fast. Both ways help the breaker act quickly and keep things safe.
Tests and data show these tripping methods work well. For example, tests on arc fault detection show some breakers can stop faults in less than eight milliseconds. The ABB Arc Vault system shows this fast action helps stop failures. Other tests collect data on voltage and current during use. Experts use this data to measure how the breaker works and if it might fail.
A circuit breaker must always be ready after a time-out. If it is not, there may be a problem with the breaker. Regular tests and smart monitoring keep the breaker working well. When the breaker trips, it goes into a time-out to protect the system. After fixing the problem, users can reset the breaker so it works again.
| Component | Function | Role in Preventing Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Frame | Holds and protects internal parts | Keeps components in safe state |
| Contacts | Open and close to control current | Stops flow during failure |
| Trip Unit | Detects faults and triggers tripping | Senses state changes |
| Operating Mechanism | Moves contacts during trip | Ensures quick time-out |
Circuit breakers are very important for keeping electrical systems safe. Their parts and tripping methods work together to find problems and stop failures. Regular updates and smart tools help circuit breakers stay safe and last a long time.
Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers come in many kinds for different places. Each type is made for homes, businesses, or big buildings. Picking the right one keeps the panel safe and power steady. The most common types are single-pole, double-pole, GFCI, AFCI, main, and branch circuit breakers. Some systems use miniature circuit breaker, molded case circuit breaker, or high-voltage circuit breaker for special jobs.
Single-Pole and Double-Pole
Single-pole and double-pole circuit breakers are used most in homes and small shops. Single-pole breakers handle 120 volts. They work well for lights, outlets, and small things. Double-pole breakers handle 240 volts. They protect big machines like ovens, dryers, and air conditioners. In 2023, double-pole breakers were used the most. This is because they protect high-voltage systems. Single-pole breakers are being used more as new homes are built.
| Aspect | Double-Pole Breaker | Single-Pole Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Handling | 240 volts, good for high-voltage systems | 120 volts, made for home use |
| Applications | Big appliances, HVAC, solar panels | Lights, outlets, small electronics |
| Advantages | Full shut-off, even protection | Cheap, small, easy to put in |
| Limitations | Bigger, costs more, harder to install | Only for small circuits, can get overloaded |
| Market Share (2023) | Most used at 42.1% worldwide | Growing fast in new homes |
Miniature circuit breaker and miniature circuit breakers are picked for these jobs. They are small, simple to put in, and work well.
GFCI and AFCI
GFCI and AFCI circuit breakers give extra safety. GFCI breakers stop power if they find a leak to the ground. This helps stop shocks in kitchens and bathrooms. AFCI breakers trip if they find dangerous arcs. These arcs can start fires in bedrooms and living rooms. Reports show GFCI and AFCI breakers help stop many fires and injuries each year. Many places now require these breakers by law. They are important for keeping homes safe.
Main vs. Branch
Main circuit breakers control all the power coming into the panel. They work like the main switch for the whole building. Branch circuit breakers protect smaller parts, like rooms or groups of outlets. High-voltage circuit breaker, air power circuit breakers, and molded case circuit breakers are used in big buildings or factories. These breakers can handle big surges and keep large systems safe.
Note: The price of circuit breakers changes by type, amperage, and how they are put in. For example, a single-pole breaker costs $100-$150. A double-pole breaker costs $150-$200. Main breakers can cost $200-$600. GFCI and AFCI breakers cost $30-$100 more than regular ones. Labor, where you live, and local rules also change the total price.
Why Circuit Breakers Trip
Overloads
A circuit breaker goes into a time-out when it senses too much power use. This happens if too many things are plugged in at once. The wires get hot, so the breaker stops the power to keep things safe. If the problem is not fixed, the breaker stays off. This helps stop bigger problems and keeps the system safe. Overloads often happen when people plug in too many appliances or use the wrong breaker size.
Short Circuits
A short circuit makes the current jump up very fast. The circuit breaker notices this and shuts off quickly. Experts say that vibration signals from breakers can help find a short circuit. These signals change the breaker’s state and make it trip. Researchers learned that short circuit currents do not keep rising forever. They reach a steady level, which helps the breaker work better. This quick action stops bigger problems and limits damage. The breaker stays off until the short circuit is fixed.
Ground Faults
A ground fault happens when electricity goes to the ground by mistake. The circuit breaker senses this and turns off to stop a problem. Most service calls for tripped breakers are because of overloads or short circuits, but ground faults also matter.
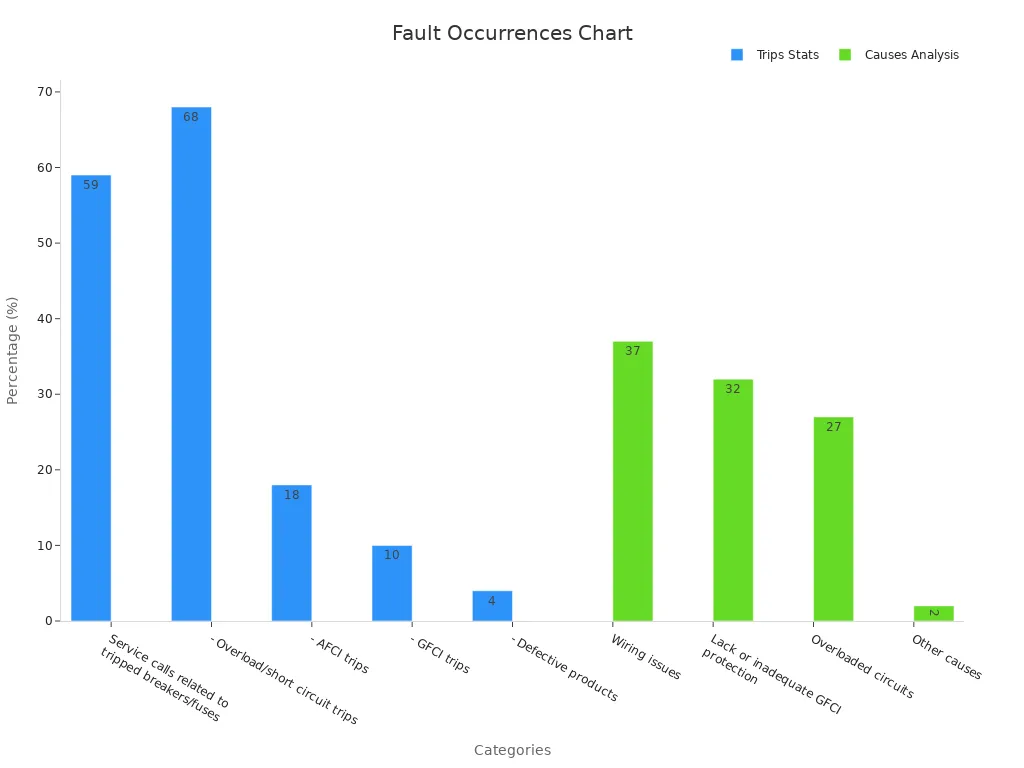
The National Electrical Code says ground fault protection is needed in many places. Breakers must turn off fast to keep people and equipment safe. Sensors can find ground faults and tell the breaker to trip, stopping more problems.
What to Do
When a circuit breaker trips, check what caused it. Look for overloads, short circuits, or ground faults. Follow these steps:
Turn off all things plugged into the circuit.
Reset the breaker to normal.
If it trips again, leave it off and call an electrician.
It is best to pick breakers with the right voltage, current rating, and interrupting power. Regular checks keep the breaker working well and stop surprise trips. This helps lower the chance of small faults turning into big problems.
| Guideline Aspect | Key Points and Data-Supported Practices |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | Make sure the breaker matches the system voltage for safety. |
| Interrupting Capacity | Pick breakers that can handle at least twice the biggest fault current. |
| Maintenance & Testing | Clean, tighten, and test often to keep breakers ready to trip if needed. |
A circuit breaker keeps the system safe by turning off during faults. This stops small problems from becoming big ones and keeps the electrical system safe.
Circuit Breakers vs. Fuses
Key Differences
Circuit breakers and fuses both keep electrical systems safe, but they do not work the same way. A fuse is used only once. If there is a problem, the fuse melts and stops electricity. After this, someone must put in a new fuse before power comes back. A circuit breaker is different. It can be reset after it trips. This means you do not need a new part, and power comes back fast.
The table below shows how circuit breakers and fuses are different:
| Protection Type | Interrupting Rating (AIC) | Fault Clearing Time (seconds) | Reset Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current-Limiting Fuse | 200,000-300,000 | 0.004 | No - requires replacement |
| Standard Circuit Breaker | 10,000-65,000 | 0.08-0.25 | Yes - manual reset |
| High-Interrupting Breaker | 100,000-200,000 | 0.05-0.16 | Yes - manual reset |
A fuse stops problems faster, but you must replace it before power returns. Circuit breakers take a little longer to trip, but you can reset them quickly. This makes it easier to get power back.
Changing a fuse takes about 30 to 45 minutes and needs a trained person. Power stays off while this happens. Resetting a circuit breaker takes about 5 minutes, so power comes back much sooner.
Advantages
Circuit breakers have many good points for today’s electrical systems. You can reset them after they trip, so you do not need to buy new parts every time. This saves money and keeps power on. Circuit breakers protect against overloads and short circuits. Fuses mostly protect against overloads. Many circuit breakers have extra safety features, like ground-fault protection, to keep everyone safe.
Circuit breakers make it simple to get power back after a problem. They help lower downtime and protect equipment.
A circuit breaker costs more at first, but it saves money later. Service teams spend less on fixing and replacing parts. Regular checks and planned repairs help stop sudden problems, so power stays on. In big buildings and factories, circuit breakers work better than fuses for complex needs. They also make it safer because there are fewer mistakes when fixing them.
A study in factories showed that using circuit breakers with smart tools lowered the cost of service and repairs. Finding problems early let teams fix things before they broke. This kept power running well. Over time, these good points made circuit breakers the best choice for safe and steady power.
Circuit Breaker Pattern in Software
Definition
The circuit breaker pattern in software helps systems work better. Developers use it to stop a service from failing over and over. If a remote service fails too much, the circuit breaker pattern puts it in time-out. This time-out stops more requests from going to the broken service. The pattern has three main states: closed, open, and half-open. In the closed state, requests go through as usual. If failures go up, the pattern switches to open. In the open state, all requests are blocked for a set time. After this, the pattern moves to half-open. In half-open, it checks if the remote service is fixed. If the service works, the pattern goes back to closed. If not, it returns to open.
Researchers like Hyslop (2014) and Schmidt & Stal (2016) say the circuit breaker pattern stops big failures in systems. The pattern uses counters and timers to change states. This keeps the system healthy and stops long outages. The circuit breaker pattern also helps the system recover by letting services rest before more requests come in.
Applications
Many companies use the circuit breaker pattern in microservices and cloud systems. When a remote service fails, the pattern quickly puts it in time-out. This stops the problem from spreading to other parts of the system. The pattern helps with health checks and sends alerts when states change. This lets teams act fast.
The circuit breaker pattern in software is not the same as hardware circuit breakers. Hardware breakers react to electrical faults very fast. The software pattern uses data to watch service health. It tracks failures, checks recovery, and helps plan repairs. For example, Bass & Klein (2017) and Hochschild & Murphy (2019) found the pattern makes microservices more reliable. Cohn (2019) shares real examples where the pattern helps systems recover after short problems.
| Aspect | Hardware Circuit Breakers | Software Circuit Breaker Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Main Role | Stops electrical faults | Prevents service failure spread |
| State | On/Off | Closed, Open, Half-Open |
| Time-out | Immediate trip | Timed block and test |
| Monitoring | Physical signals | Service health, failure rates |
| Recovery | Manual reset | Automatic or manual reset |
The circuit breaker pattern in software keeps services healthy. It helps systems recover and stops big failures. It uses time-outs, health checks, and monitoring to protect remote calls and make the system stronger.
Circuit breakers are very important for keeping people and things safe. They watch each circuit, find problems, and help protect everyone. In 2024, there are more than 20 million circuit breakers in use. By 2033, this number may grow to over 35 million. The market is getting bigger because of smart grids and new safety rules.
| Metric | Value/Trend |
|---|---|
| Units Installed (2024) | 20+ million |
| Projected (2033) | 35+ million |
| Market Value (2025) | $5 billion |
| Safety Impact | Fault prevention, fire risk reduction, real-time state monitoring |
Knowing how a circuit breaker works helps keep things safe. It is good to know why it trips and how its state changes. Newer models use real-time data to fix problems faster. They also help lower the time when power is out. Putting them in the right way and checking them often keeps the system working well. Studies show that looking at breakers, testing them, and watching their state helps them last longer. As technology gets better, smart circuit breakers will make things even safer. Learning about new features and taking care of the system helps keep everyone safe.
Circuit breakers stop problems and help things work again fast.
Smart tools watch each circuit’s state for quick action.
Checking and installing them right keeps protection strong.
FAQ
What does a circuit breaker do in an electrical service?
A circuit breaker keeps the electrical service safe by turning off power if it finds a problem. It protects the service from too much current, short circuits, and ground faults. This helps stop fires and keeps devices from getting damaged.
How often should someone check a circuit breaker in a service panel?
Experts say to check the circuit breaker in a service panel once every year. Checking often helps the service work well. If the service trips a lot, have a professional look at it right away.
Can a circuit breaker be used in every type of service?
Most homes and businesses use a circuit breaker in their service. Some old services still use fuses instead. Modern service panels almost always use circuit breakers because they are safer and easy to reset after a problem.
Why does a circuit breaker trip in a service?
A circuit breaker trips in a service if it senses too much current, a short circuit, or a ground fault. This keeps the service from getting too hot or damaged. People can reset the breaker after fixing what caused the problem.
What should someone do if the service loses power and the circuit breaker will not reset?
If the service loses power and the circuit breaker will not reset, unplug everything from the service. Try to reset the breaker again. If it still does not work, call a licensed electrician. There may be a big problem that needs expert help.
Related Articles
-
HV DC Contactors: The Backbone of Efficient EV Charging Systems
-
Choosing the Right Molded Case Circuit Breaker for Industrial and Photovoltaic Applications
-
How to Choose the Right Plug, Socket, and Outlet for Your Electrical Needs
-
The Comprehensive Guide to Circuit Breakers: Applications, Types, and Benefits
-
What is the Difference Between a Molded Case Circuit Breaker and an Insulated Case Circuit Breaker?
-
What is the Life Expectancy of a Molded Case Circuit Breaker?



















